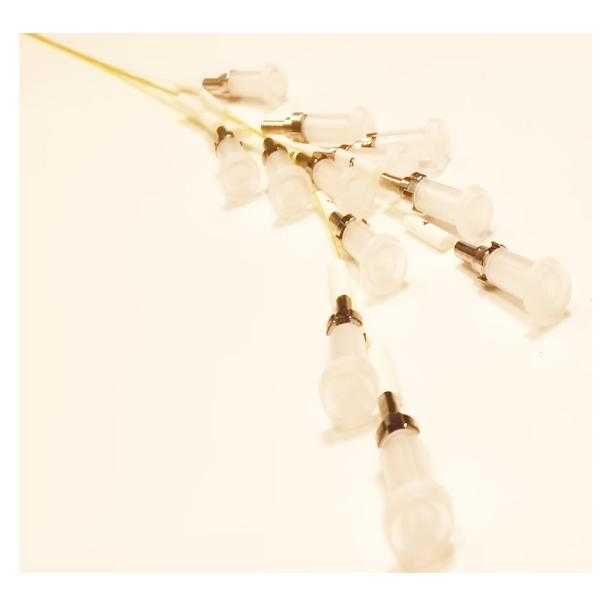
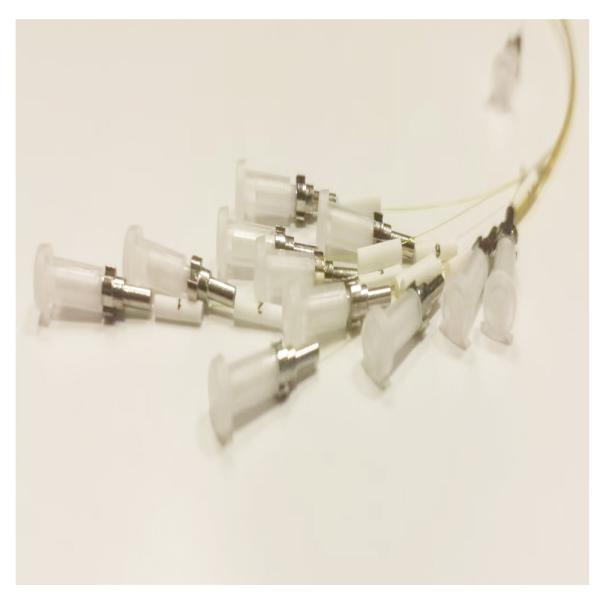
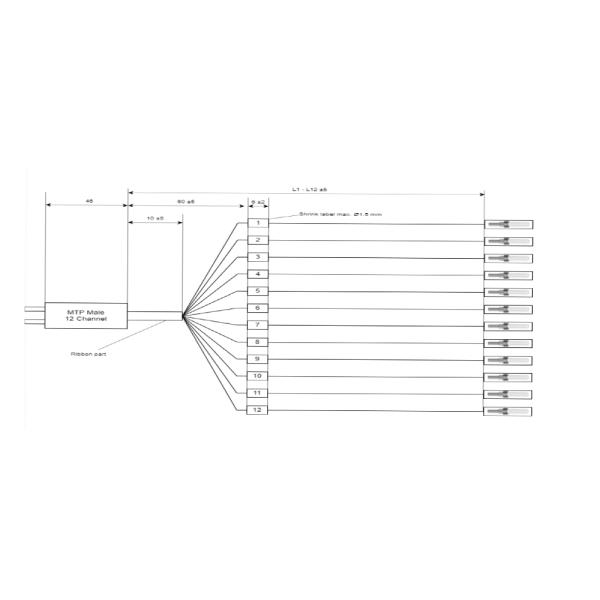
High temperature MPO (Multi-fiber Push-On) cables are specialized
optical fiber cables designed to withstand elevated temperatures,
making them suitable for harsh environments where standard cables
might fail.
Below is a detailed overview of their characteristics,
applications, and key considerations:
An MPO cable is a multi-fiber connector system that uses a push-on
mechanism to connect multiple optical fibers (typically 12, 24, or
more fibers) in a single connector. High-temperature versions are
engineered with materials and construction that enable them to
operate reliably in extreme heat, often up to 125°C or higher (standard MPO cables usually have a temperature range of -20°C to
70°C).
Temperature Resistance
- Jacket Material: Often made of fluoropolymers (e.g., PTFE, FEP) or silicone
rubber, which retain flexibility and insulation properties at high
temperatures.
- Armor/Reinforcement: Stainless steel braiding or aramid fibers (e.g., Kevlar) to
protect against heat, abrasion, and mechanical stress.
- Fiber Coatings: Specialized heat-resistant coatings (e.g., polyimide) around the
optical fibers to prevent degradation.
Connector Design
- MPO connectors for high-temperature applications may use ceramic or
metal ferrules (instead of plastic) to maintain precision alignment
in thermal stress.
- Heat-resistant adhesives and seals prevent moisture ingress and
connector degradation.
Multi-Fiber Integration
- Supports high-density fiber counts (e.g., 12-fiber, 24-fiber, or
72-fiber arrays) for high-bandwidth applications in tight spaces.
- Reliability in Extreme Conditions
- Resists melting, charring, or signal loss due to heat, ensuring
consistent data transmission.
- Longer Lifespan
- Reduces maintenance and replacement costs in high-temperature
environments where standard cables degrade quickly.
- Space and Weight Efficiency
- High-density multi-fiber design minimizes cabling bulk, crucial in
tight, heat-prone spaces.
- Chemical Resistance
- Fluoropolymer jackets often resist oils, solvents, and corrosive
chemicals found in industrial settings.
- Temperature Range
- Verify the cable’s rated operating temperature (e.g., -40°C to
125°C) matches the application’s needs.
- Bend Radius
- High-temperature materials may have stiffer jackets, so ensure the
cable can bend without damaging fibers (typically ≥10x the cable
diameter).
- Insertion Loss and Return Loss
- Check optical performance specifications (e.g., insertion loss
≤0.3dB, return loss ≥55dB) to meet bandwidth requirements.
- Certification and Compliance
- Look for industry standards compliance (e.g., Telcordia GR-326 for
optical cables, UL 94 for flammability, or military specs like
MIL-DTL-83446).
- Avoid Mechanical Stress
- Use specialized tools for terminating high-temperature MPO
connectors to prevent damage from heat or pressure.
- Thermal Management
- Route cables away from direct heat sources when possible, or use
heat shielding for added protection.
- Testing
- Perform optical loss testing after installation to ensure no
degradation from temperature exposure.
Hicorpwell High-temperature MPO cables are essential for enabling
reliable optical connectivity in sectors where heat would otherwise
disrupt communication or data systems. Their specialized design
balances durability, performance, and thermal stability to meet the
demands of extreme operating conditions.